- The dual drive of policies and markets has jointly spurred the expansion of energy storage battery production
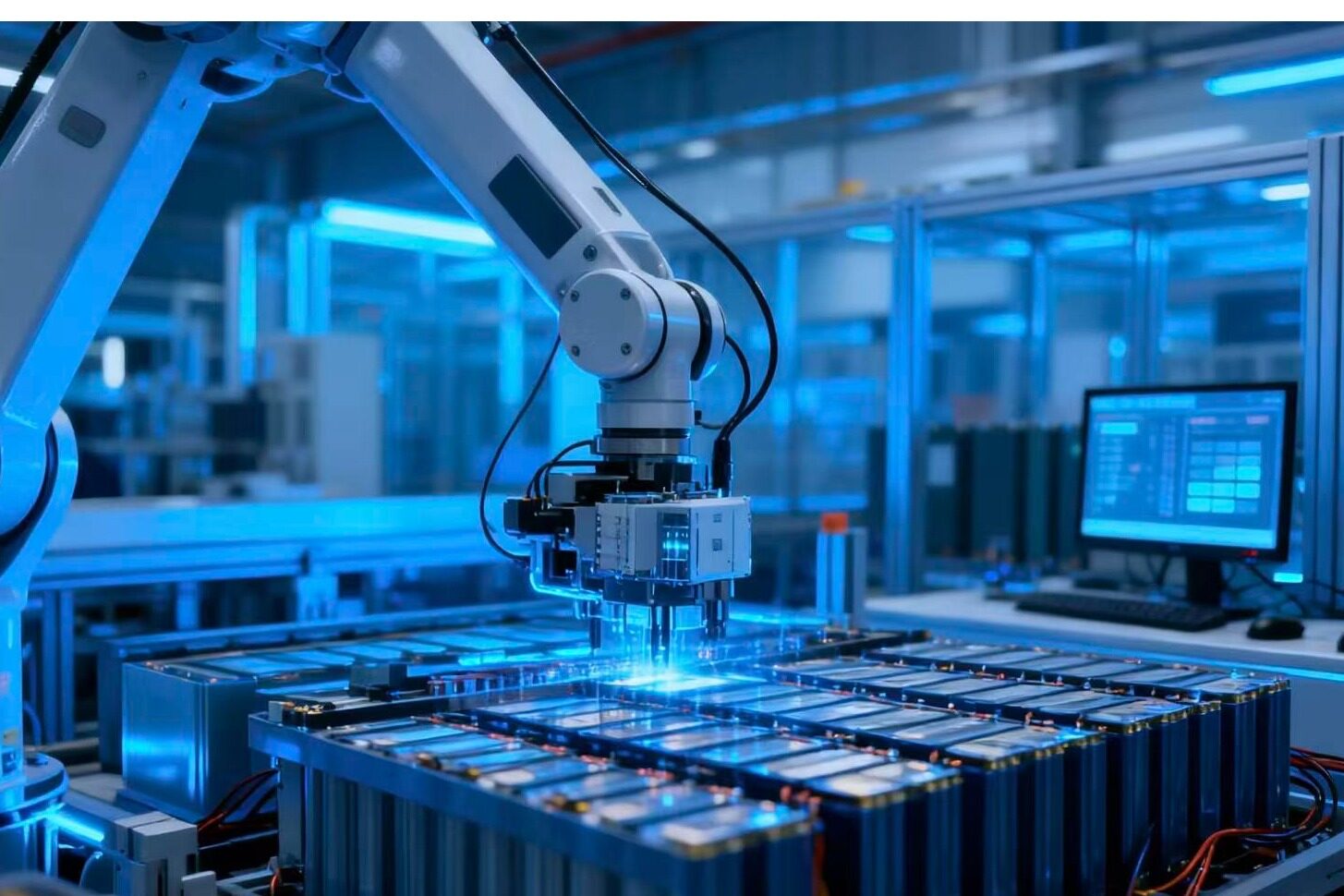

Against the backdrop of accelerating global energy transition, energy storage, as the core support for new energy consumption and stable operation of the power grid, has seen explosive growth in market demand. Accompanying it is the energy storage battery cell - the core component of this energy storage system, which is experiencing an unprecedented expansion boom. From top enterprises investing billions of dollars to small and medium-sized enterprises joining the competition, the competition for battery cell production capacity is becoming increasingly fierce. The wave of expansion sweeping the industry is not accidental, but the inevitable result of multiple factors such as policy dividends and market demand resonance, technological iteration, and industrial chain synergy. Its underlying driving force clearly points to the core demands of global energy transformation and the inherent logic of industrial development.
The strong guidance from the policy side has built a "ballast stone" for the expansion of energy storage cell production. Major economies around the world have incorporated energy storage into their energy strategy layouts, forcing the large-scale development of the energy storage industry through policy subsidies, mandatory storage allocation, and market mechanism construction. At the domestic level, under the "dual carbon" goal, the mandatory allocation and storage policy for new energy power stations has been popularized nationwide. The construction of large-scale wind and solar power bases and new power systems clearly requires supporting energy storage facilities. At the same time, local governments have intensively introduced subsidies, tax incentives, and capacity implementation support policies for energy storage projects, directly activating the demand for energy storage markets. For example, new energy provinces such as Qinghai and Gansu require new wind and photovoltaic projects to have a storage ratio of no less than 10% and a duration of no less than 2 hours, which has led to a massive demand for battery cells. In the international market, the European Union's Key Raw Materials Act includes energy storage cells in the category of strategic goods, while the United States provides high tax credits for domestic energy storage projects through the Inflation Reduction Act, promoting the continuous expansion of global energy storage market demand. The combination of rigid policy constraints and incentive measures has transformed the demand for energy storage battery cells from "optional" to "mandatory". In order to seize the policy dividend window, enterprises have increased their production.
The explosive growth in the market has injected a "stimulant" into the expansion of energy storage cell production. With the continuous increase in installed capacity of renewable energy such as wind power and photovoltaics, the demand for peak shaving, frequency regulation, and valley filling of energy storage in the power grid is becoming increasingly urgent. In addition, with the rapid rise of emerging application scenarios such as industrial and commercial energy storage, household energy storage, and microgrids, the demand for energy storage cells in the market is showing exponential growth. Data shows that the global demand for energy storage cells will exceed 300GWh in 2023, and is expected to exceed 500GWh in 2024, with a compound annual growth rate of over 40% for the next three years. The surge in demand has directly led to a tight supply of battery cells, with orders for some specifications taking 6-12 months to complete. The situation of "one chip in short supply" has forced companies to accelerate production expansion. At the same time, the application scenarios of energy storage cells are constantly expanding, extending from traditional grid side energy storage to fields such as transportation, communication, and data centers. Diversified demand further opens up space for capacity growth. For example, the popularity of household energy storage in the European and Southeast Asian markets has driven the growth in demand for miniaturized and high safety battery cells; Industrial and commercial energy storage places higher demands on the large capacity and long cycle life of battery cells, stimulating enterprises to expand production and adapt products accordingly.
The virtuous cycle of technological iteration and cost reduction provides an accelerator for the expansion of energy storage cell production. In recent years, energy storage cell technology has continuously broken through, and mainstream technology routes such as ternary lithium and lithium iron phosphate have been continuously optimized. Core indicators such as energy density, cycle life, and safety have significantly improved. Lithium iron phosphate has become the mainstream choice for energy storage batteries due to its advantages of low cost, long cycle, and high safety. The application of new electrolytes and diaphragm materials further enhances the performance limit of batteries. Technological progress has driven the continuous reduction of battery cell costs. In the past five years, the unit cost of energy storage batteries has decreased by more than 60%, significantly improving the economic efficiency of energy storage projects. In turn, this has stimulated market demand, forming a virtuous cycle of "technological progress - cost reduction - demand growth - capacity expansion". In addition, the automation and intelligence level of battery cell production equipment continues to improve, the construction cycle of production lines is shortened, and the speed of capacity ramp up is accelerated, which also provides technical support for enterprises to rapidly expand production. Through large-scale R&D investment, leading enterprises have mastered the core technology of battery cells, formed technical barriers, and gained a first mover advantage in the expansion process, further driving the upgrading of production capacity throughout the industry.

The synergy of the industrial chain and capital support have cleared the "obstacles" for the expansion of energy storage cell production. As the core link of the energy storage industry chain, the expansion of energy storage cells relies on the collaborative cooperation between upstream and downstream. On the upstream side, the production capacity of key raw materials such as lithium, cobalt, and nickel is gradually released, and the stability of raw material supply is improved, providing resource guarantees for the expansion of battery cell production; In terms of midstream, battery cell production equipment suppliers are accelerating their capacity layout to meet the equipment needs of enterprise expansion; On the downstream side, energy storage system integrators, terminal application companies, and battery cell companies have signed long-term supply agreements to lock in production capacity and reduce market risks for enterprise expansion. At the same time, the capital market's attention to the energy storage track continues to heat up, and companies have obtained sufficient funds through IPO, private placement, bond issuance and other means, providing financial support for expansion projects. For example, several leading battery cell companies have raised billions of yuan through private placement to build new battery cell production lines and technology research and development centers, accelerating capacity expansion and technological upgrades.
It is worth noting that behind the expansion boom, the industry is also facing challenges such as overcapacity risk, technological route iteration, and fluctuations in raw material prices. Some small and medium-sized enterprises blindly follow the trend to expand production, which may lead to overcapacity in low-end production, while there is still a gap in high-end production capacity; The rapid iteration of technological routes may also put some outdated production capacity at risk of being eliminated. Therefore, enterprises need to maintain rationality in the process of expanding production, focus on technological innovation and product upgrading, accurately match market demand, and avoid blind expansion.
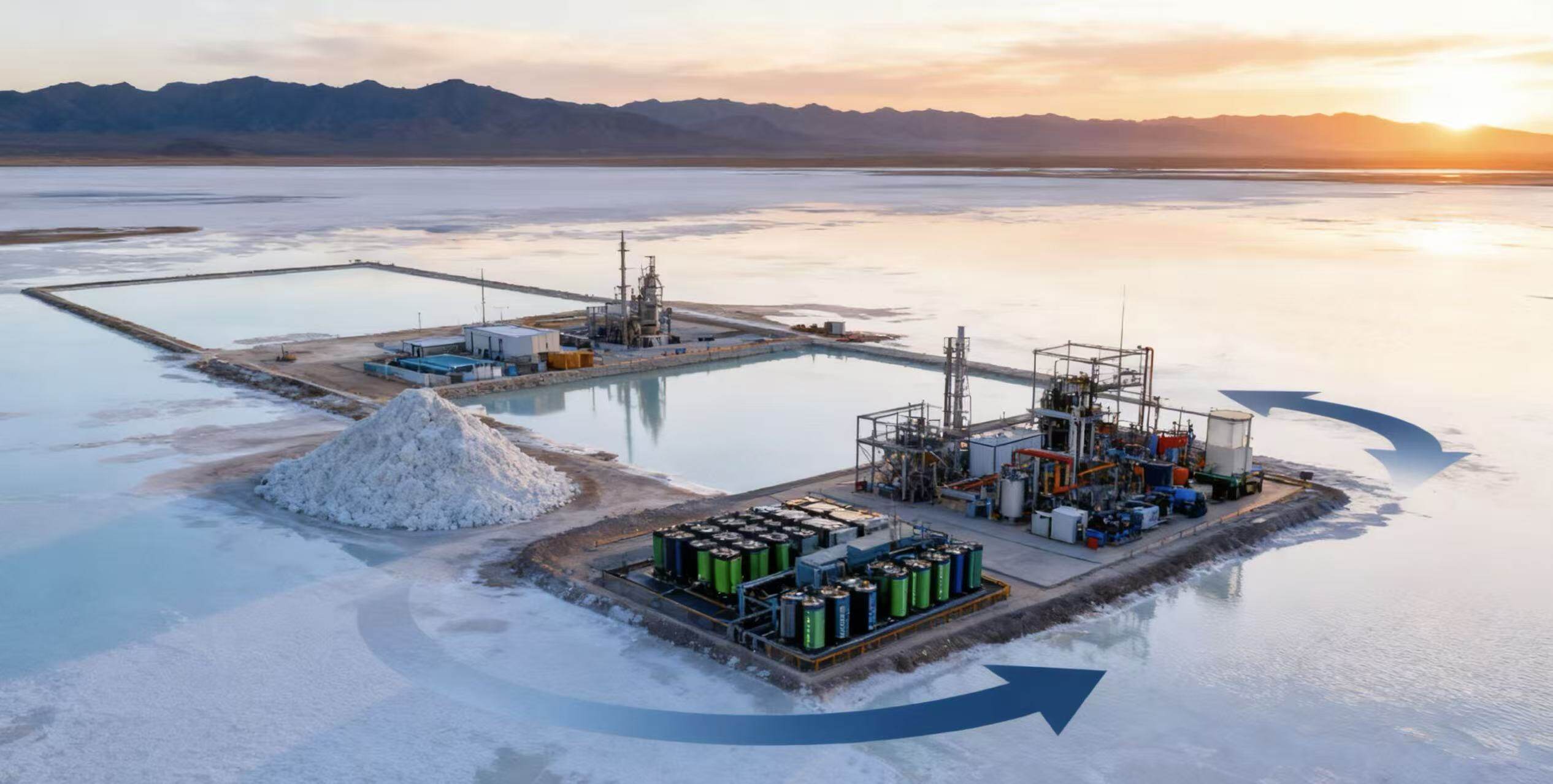

Overall, the dual drive of policies and markets, as well as the deep empowerment of technology and capital, have jointly spurred a wave of expansion in the production of energy storage batteries. This wave is not only an inevitable choice for the industry to respond to current market demand, but also an important symbol for the energy storage industry to move towards large-scale and high-quality development in the context of global energy transformation. In the future, with the continuous advancement of technology and the continuous improvement of the industrial chain, the production capacity of energy storage cells will be further released, providing more solid support for the global energy transformation.Editor/Bian Wenjun
Comment
 Praise
Praise
 Collect
Collect
 Comment
Comment
 Search
Search














Write something~